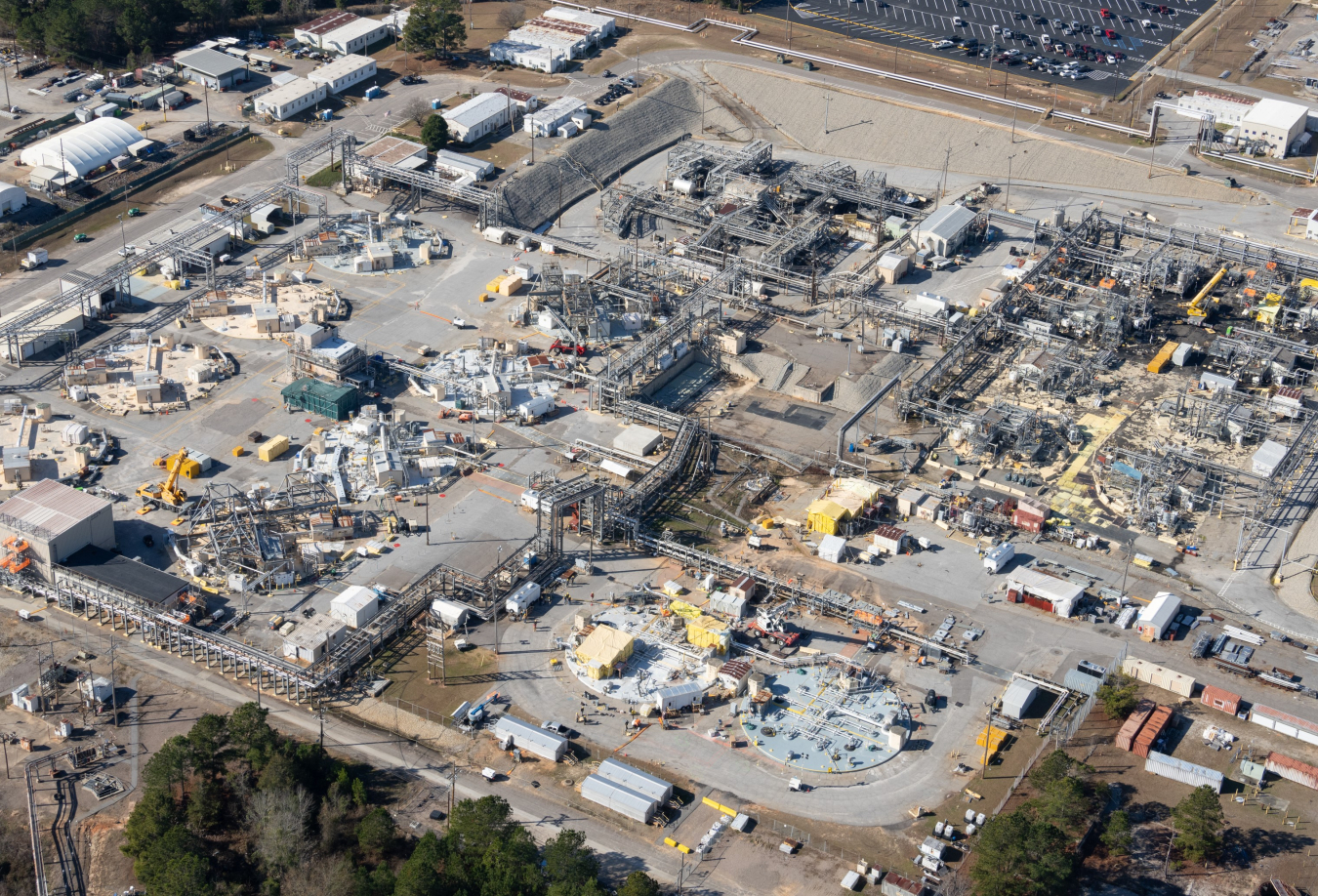
The Savannah River Site’s F Tank Farm, where Tank 4 completed preliminary cease waste removal a year ahead of schedule. (Photo: DOE)
The Department of Energy’s Office of Environmental Management said it has reached a regulatory milestone ahead of schedule in preparing radioactive waste tanks for closure at the Savannah River Site in South Carolina. DOE-EM said it received concurrence in January from the South Carolina Department of Environmental Services (SCDES) and the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency that SRS had successfully removed waste from the site’s Tank 4 and may now proceed to waste sampling and analysis of that tank ahead of its closure.
Testing is conducted at the Hanford Site’s Waste Treatment and Immobilization Plant. (Photo: DOE)
The Department of Energy has agreed to hold a 30-day review and comment period on a draft environmental analysis associated with a proposed plan for retrieving, grouting, and transporting some of Hanford’s low-activity tank waste for out-of-state disposal.
IWTU operators monitor radiological operations during the current waste treatment campaign at the Idaho National Laboratory Site facility. (Photo: DOE)
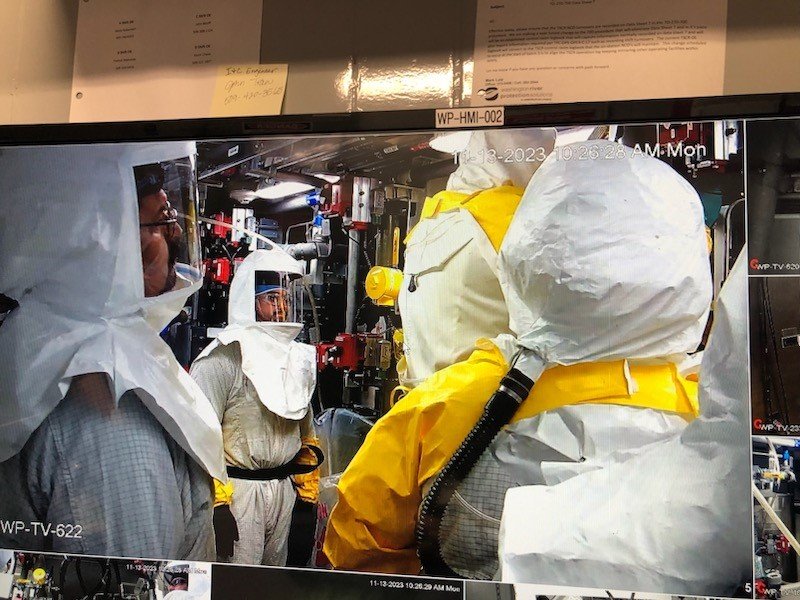
As of last week, crews with Department of Energy cleanup contractor Idaho Environmental Coalition (IEC) processed more than 142,000 gallons of radioactive sodium-bearing tank waste at Idaho’s Integrated Waste Treatment Unit (IWTU) this year.
Using cameras placed inside a temporary shelter, nuclear chemical operator Joe McCoy monitors the pretreatment activities of the Hanford Site’s TBI demonstration. (Photo: DOE-EM)
The Department of Energy’s Office of Environmental Management said that contractors have completed the treatment of 2,000 gallons of radioactive and chemical waste as part of the Hanford Site’s Test Bed Initiative project, which aims to demonstrate the feasibility of alternative options for retrieving and treating low-activity tank waste at the site in Washington state.
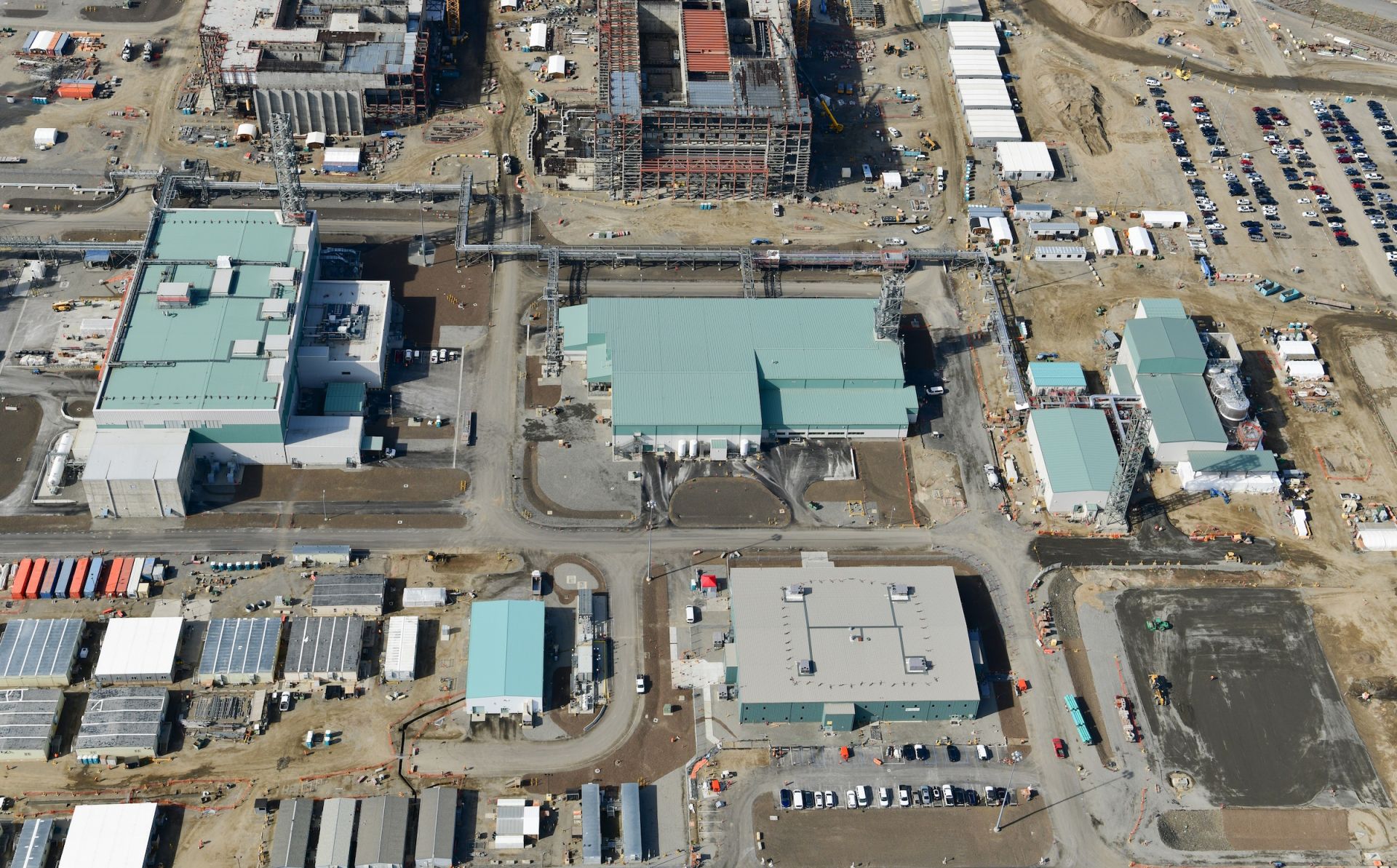
Hanford’s Waste Treatment and Immobilization Plant, also known as the Vit Plant. (Photo: Bechtel National)
BWX Technologies announced that the Department of Energy has approved Hanford Tank Waste Operations & Closure (H2C) to begin work under a contract valued at up to $45 billion to clean up tank waste at the Hanford Site near Richland, Wash. H2C is a limited liability company made up of BWXT Technical Services Group, Amentum Environment and Energy, and Fluor Federal Services.
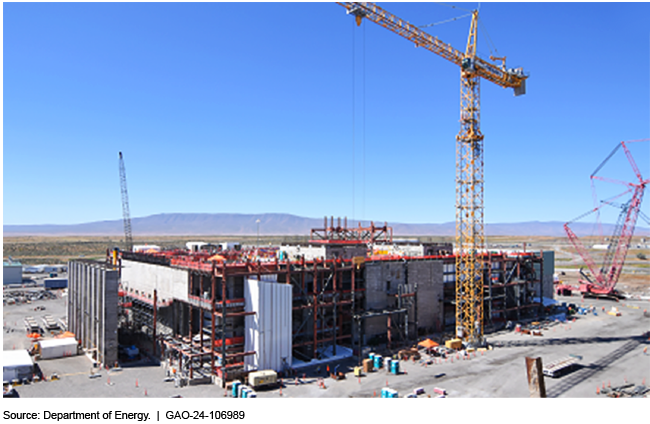
Hanford’s HLW Facility under construction in early 2024. (Photo: Bechtel National)
The Government Accountability Office has recommended that the Department of Energy put a hold on construction of its High-Level Waste Facility at the Hanford Site near Richland, Wash. The GAO said design and construction of the facility, part of Hanford’s Waste Treatment and Immobilization Plant, also known as the Vit Plant, should be paused until several actions are taken, including considering other alternatives for managing the site’s high-level radioactive liquid waste.
Crews with the Idaho National Laboratory Site’s IWTU replace filter bundles inside the unit’s process gas filter. (Photo: DOE)
The Department of Energy’s Office of Environmental Management announced yesterday that waste processing operations have resumed at the Integrated Waste Treatment Unit (IWTU) at the Idaho National Laboratory Site. The resumption of operations follows the completion of two maintenance campaigns at the radioactive liquid waste treatment facility.
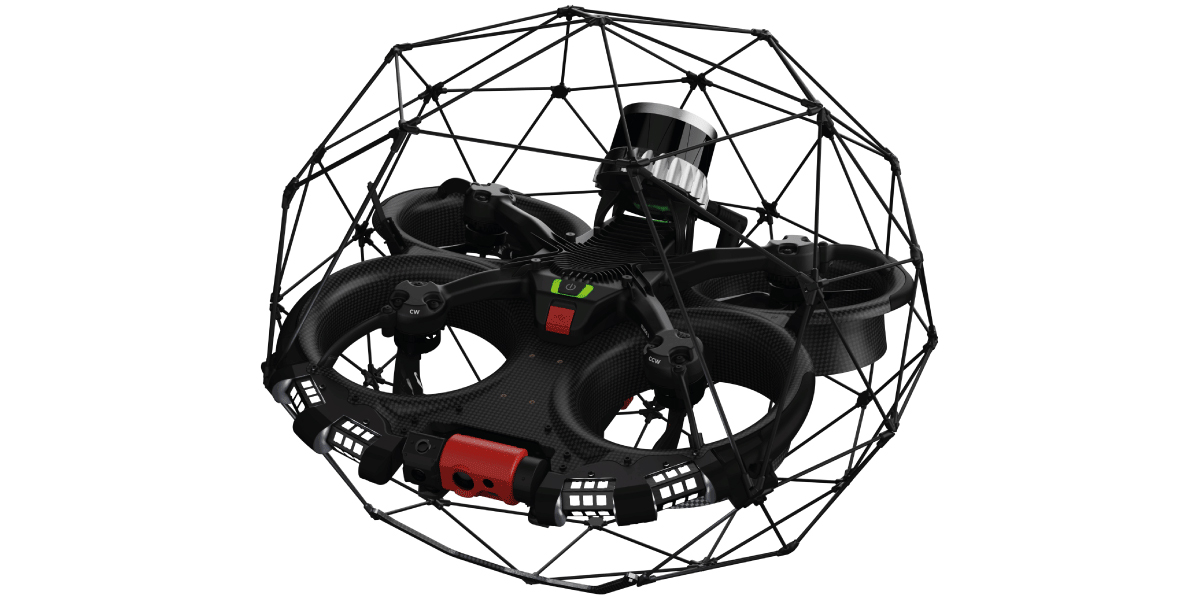
SRS liquid waste contractor Savannah River Mission Completion will use drones equipped with cameras to inspect the cleaning status of waste tanks at the site. (Photo: DOE)
The Department of Energy’s Office of Environmental Management will begin using drones for the first time to internally inspect radioactive liquid waste tanks at the department’s Savannah River Site in South Carolina. Inspections were previously done using magnetic wall-crawling robots.
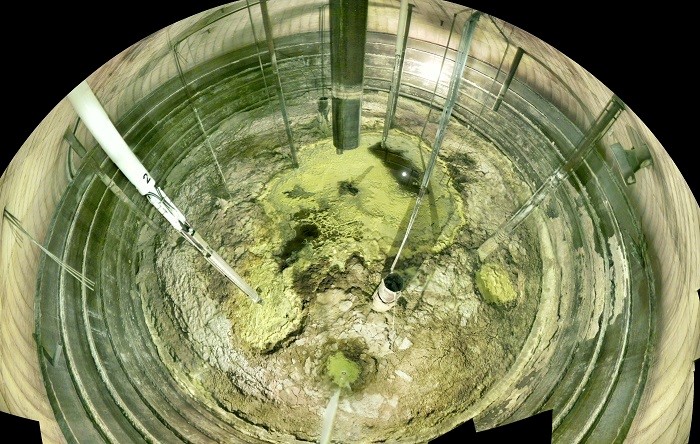
A June 2024 photo shows solid waste inside the single-shell Tank A-101 at the Hanford Site’s A Tank Farm. (Photo: DOE)
Work crews have started retrieval of radioactive and chemical waste from a third set of underground storage tanks at the Hanford Site, according to the Department of Energy's Office of Environmental Management. Contractor Washington River Protection Solutions (WRPS) is retrieving and transferring more than 325,000 gallons of waste from the single-shell Tank A-101 at the site's A Tank Farm. The waste is being sent to a newer double-shell tank for continued safe storage.
Retrieval activities began one month after workers emptied the site’s 21st single-shell tank. Waste removed from the 21 tanks totals about 3 million gallons.
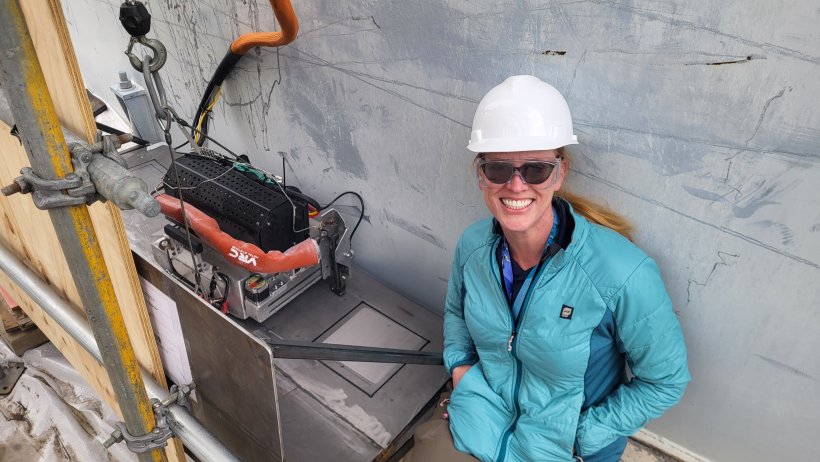
Stephanie Doll of WRPS poses next to the metal patch applied during the demonstration. (Photo: DOE)
The Department of Energy’s Office of Environmental Management and its contractor Washington River Protection Solutions (WRPS) recently demonstrated the use of cold spray technology as a means of refurbishing double-shell waste tanks at the Hanford Site in Washington state. The tanks store liquid radioactive and chemical waste that was created during Hanford’s plutonium production era.
Hanford’s Waste Treatment and Immobilization Plant, also known as the Vit Plant. (Photo: Bechtel National)
Researchers at the Department of Energy’s Argonne National Laboratory are investigating the details of plutonium chemistry with the goal of aiding the cleanup of the Hanford Site in Washington state. For more than 40 years, reactors located at Hanford produced plutonium for America’s defense program, resulting in millions of gallons of liquid radioactive and chemical waste.
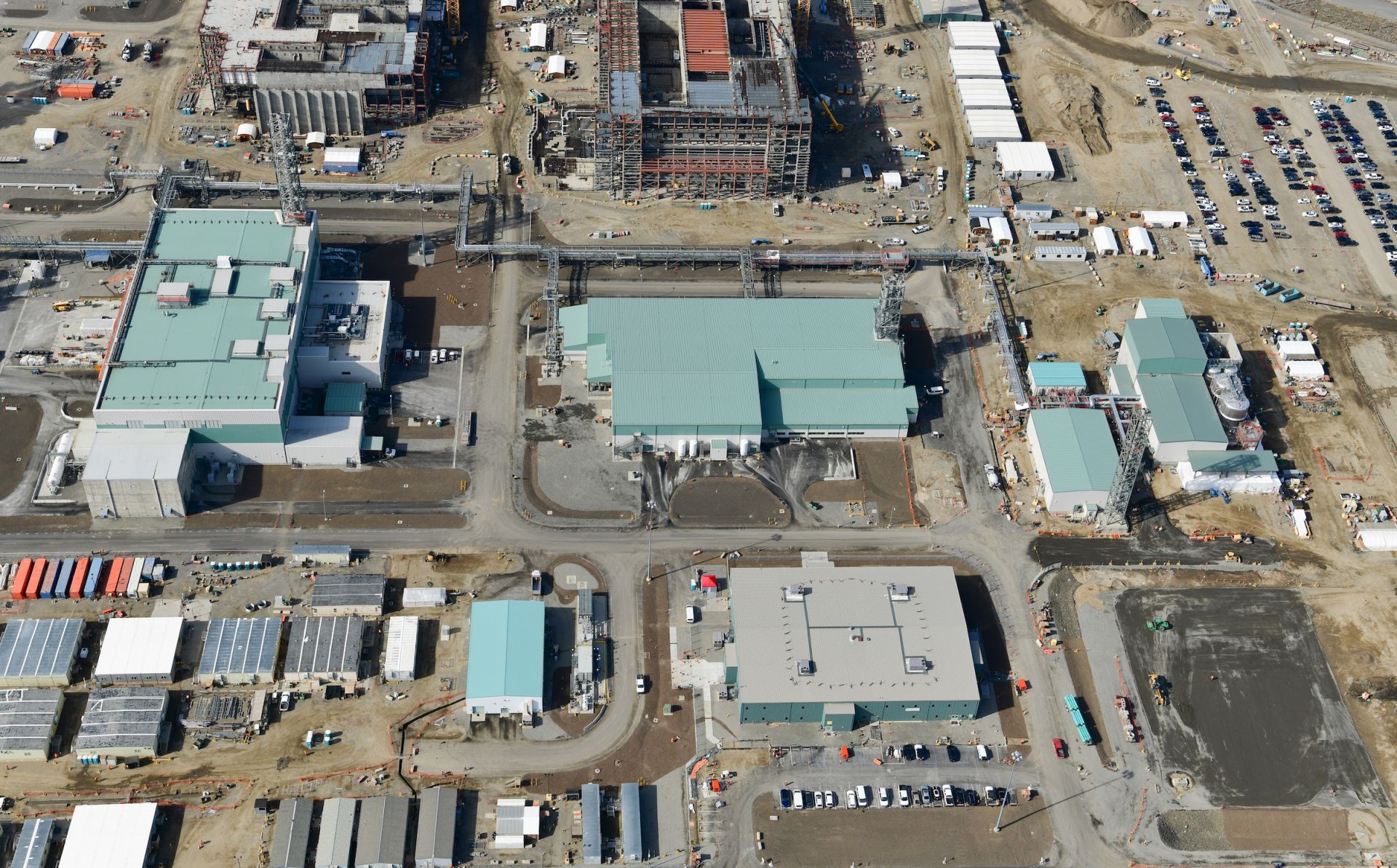
An aerial view of the Hanford Site’s 200 Area and the Waste Treatment and Immobilization Plant, also known as the Vit Plant. (Photo: DOE)
The U.S. Department of Energy, Washington State Department of Ecology, and U.S. Environmental Protection Agency have reached an agreement on revised plans for managing millions of gallons of radioactive and chemical liquid waste stored in 177 underground tanks at the Hanford Site near Richland, Wash.
Upgrades are under way at the Hanford Site's 222-S Laboratory, including replacing the Cold War-era windows in the labs hot cells. Photo: DOE)
Hanford’s Waste Treatment and Immobilization Plant, also known as the Vit Plant. (Photo: Bechtel National)
The Department of Energy’s Office of Environmental Management once again awarded a 10-year, $45 billion contract to Hanford Tank Waste Operations and Closure (H2C) of Lynchburg, Va., for the cleanup of tank waste at the Hanford Site.
A monitor in the control room of the Hanford Site’s TSCR system shows workers performing maintenance inside the TSCR facility. (Photo: DOE)
The Department of Energy Office of Environmental Management’s Office of River Protection and contractor Washington River Protection Solutions have completed the first waste processing campaign through the Tank-Side Cesium Removal (TSCR) system at the Hanford Site.
The 2F Evaporator at SRS. (Photo: Savannah River Site Photography)
The Department of Energy’s Office of Environmental Management is responsible for roughly 90 million gallons of radioactive liquid waste at Idaho National Laboratory, the Hanford Site in Washington state, and the Savannah River Site in South Carolina. About 900,000 gallons of waste are stored at INL, 56 million gallons at Hanford, and roughly 36 million at SRS. A further 400,000 gallons of waste from various operations are being stored at the Oak Ridge Site in Tennessee.
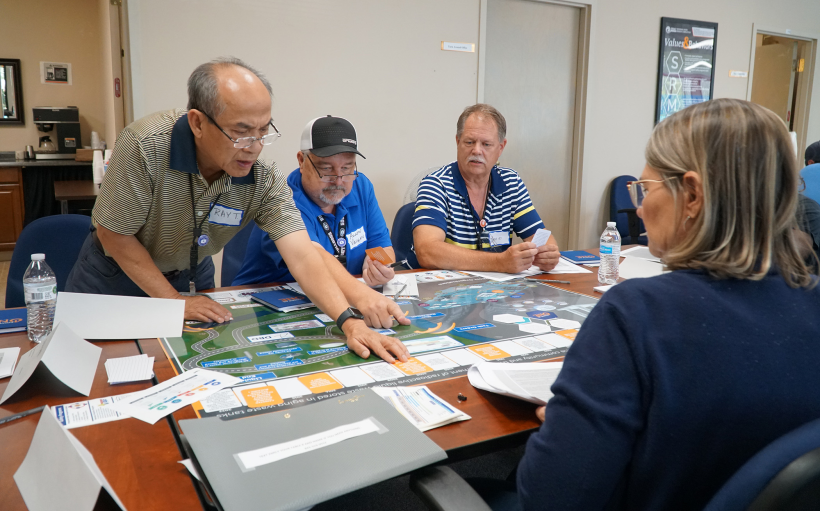
Ray Tran, an engineer for Savannah River tank farms, helps complete a timeline of SRS historical events as part of SRMC’s vision casting training initiative. (Photo: DOE)
More than 3,000 employees with Department of Energy contractor Savannah River Mission Completion (SRMC) participated in a vision casting initiative, learning more about the past, present, and future of the Savannah River Site’s liquid waste mission.
Some of the participants of the recent SRNL-Hanford Analytical Knowledge Sharing Workshop pause for a photo. (Photo: DOE)